Global Markets React Sharply to Trade Tensions
Economic Update
U.S. manufacturing activity contracted in March to 49 percent after two consecutive months of expansion. This decline, driven by weakened demand and output, led to drops in new orders, production, and employment indices. We point out that emergency interest-rate cuts are highly unusual and were last deployed by the Fed in 2020 in light of the COVID-19 pandemic. Amid potential inflation risks and slowing growth, the Fed’s May meeting will be closely watched.
State of Corporate Credit
Distressed debt exchanges (DDEs) have become the dominant form of loan default in the U.S. In 2024, DDEs outnumbered bankruptcies by more than four to one, a trend fueled by liability management transactions and expected to continue this year. We want to highlight that DDEs seldom yield lasting improvements in credit quality, as evidenced by the numerous companies that have re-defaulted through missed payments, subsequent DDEs, or bankruptcy filings.
Insolvencies
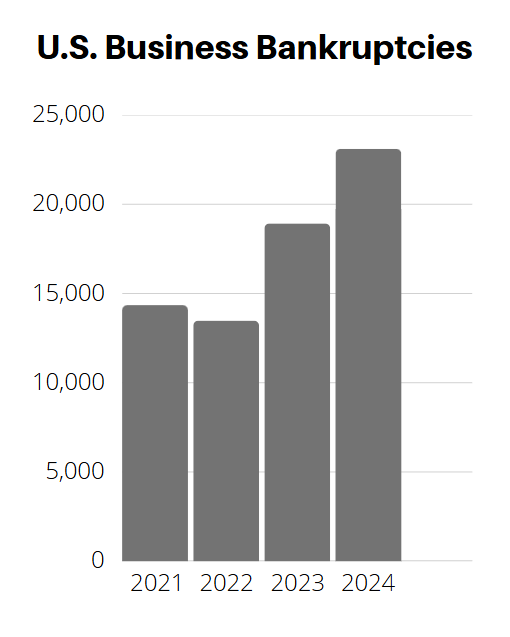
U.S. commercial chapter 11 bankruptcy filings increased 20 percent in March year over year, indicating growing economic pressures. Another concerning trend is bankruptcy filings made by U.S. companies backed by private equity and venture capital climbed more than 15% to 110 in 2024, the highest annual total on record, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence data. Canadian business bankruptcies in the 12-month period that ended January 31, 2025 were 11.7% higher than the 12-month period that ended January 31, 2024. With slowing global growth and increasing recession risks, further increases in bankruptcies are likely
Current & Evolving Credit Risks
Recession Odds Increase
Recession probabilities priced into the markets have risen significantly. The Russell 2000 now reflects a 79% probability of a recession in the U.S., while a moderate recession scenario is nearly 100% priced in. In light of heightened trade policy uncertainty, J.P. Morgan Research has also raised the probability of a global recession to 40%.
Force Majeure
Airline supplier Howmet Aerospace informed customers it declared a force majeure event, effectively claiming the right to halt shipments if they are affected by U.S. tariff policy. Force majeure is a legal practice that allows contracted parties to avoid obligations due to unavoidable or unpredictable external circumstances. Companies sometimes invoke this clause to mitigate price increases from tariffs, trade wars, and other government actions. This trend, observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, warrants attention in 2025, as companies have already declared or threatened to declare force majeure. If you receive a force majeure notice, carefully review both the contract language and the notice itself to ascertain if the stated event legally qualifies as force majeure.
Michigan Economy
Nearly 20% of Michigan’s economy is tied to the auto industry, which is preparing for tariff headwinds. Anderson Economic Group, a Michigan consulting firm, estimates the tariffs will add $2,500 to $12,000 to the price of many new cars. That will push new vehicles further beyond the reach of consumers and cause production shutdowns.



